If you suspect or have been diagnosed with a vitamin D3 deficiency, it’s essential to take steps to address it.
Vitamin D3 deficiency occurs when there is an inadequate amount of vitamin D3 in the body. Vitamin D3, also known as cholecalciferol, is a fat-soluble vitamin that is essential for various physiological functions, including maintaining healthy bones, supporting the immune system, and regulating calcium and phosphorus levels.
How much vitamin D should you get?
- 600 IU (international units) a day for people ages 1 to 70, including women who are pregnant or breastfeeding
- 800 IU a day for anyone over 70
Some experts think that these recommendations are too low, especially for people who are more likely to get the bone-thinning disease osteoporosis.
Ask your doctor how much vitamin D is best for you.
Here are some tips to help you manage and overcome vitamin D3 deficiency:
- Get tested: The first step is to confirm if you have a vitamin D3 deficiency. Ask your healthcare provider for a blood test to measure your serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels (25(OH)D). This will determine the severity of the deficiency and guide the appropriate treatment plan.
- Sunlight exposure: Spending time in direct sunlight can help your skin produce vitamin D3. Aim for 10-30 minutes of sunlight exposure on your face, arms, and legs at least twice a week. However, keep in mind that the ability to synthesize vitamin D3 from sunlight depends on factors such as geographical location, skin color, and season.
- Dietary sources: Incorporate foods rich in vitamin D3 into your diet. Good sources include fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel, tuna), egg yolks, fortified dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese), and fortified plant-based alternatives (e.g., soy milk, almond milk).
- Vitamin D3 supplements: If your deficiency is significant or your doctor recommends it, consider taking vitamin D3 supplements. The dosage will depend on your individual needs, so it’s essential to follow your healthcare provider’s advice. Vitamin D supplements are available in various forms, such as capsules, tablets, and liquid drops.
- Take it with fat: Vitamin D3 is fat-soluble, so taking it with a meal containing some healthy fats may enhance absorption. For example, take the supplement with a meal that includes nuts, avocado, olive oil, or fish.
- Be consistent: If you are prescribed vitamin D3 supplements, take them regularly and follow the recommended dosage. Consistency is crucial to maintaining stable vitamin D3 levels.
- Monitor your levels: Periodically retest your vitamin D3 levels to track your progress and ensure that your supplementation or lifestyle changes are effectively addressing the deficiency.
- Address underlying health issues: Certain medical conditions, medications, and lifestyle factors can contribute to vitamin D3 deficiency. Work with your healthcare provider to identify and address any underlying causes.
- Avoid excessive supplementation: While it’s important to address a deficiency, excessive vitamin D3 intake can lead to toxicity. Stay within the recommended dosage as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet or starting a new supplement regimen, as individual needs can vary based on factors like age, sex, health status, and existing medical conditions.
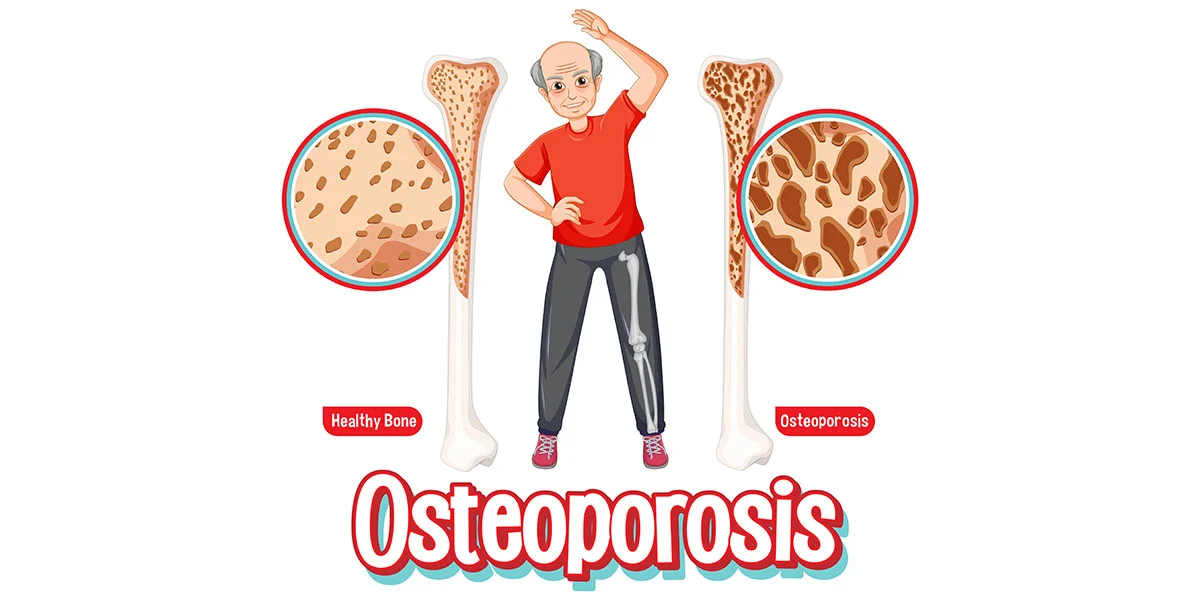
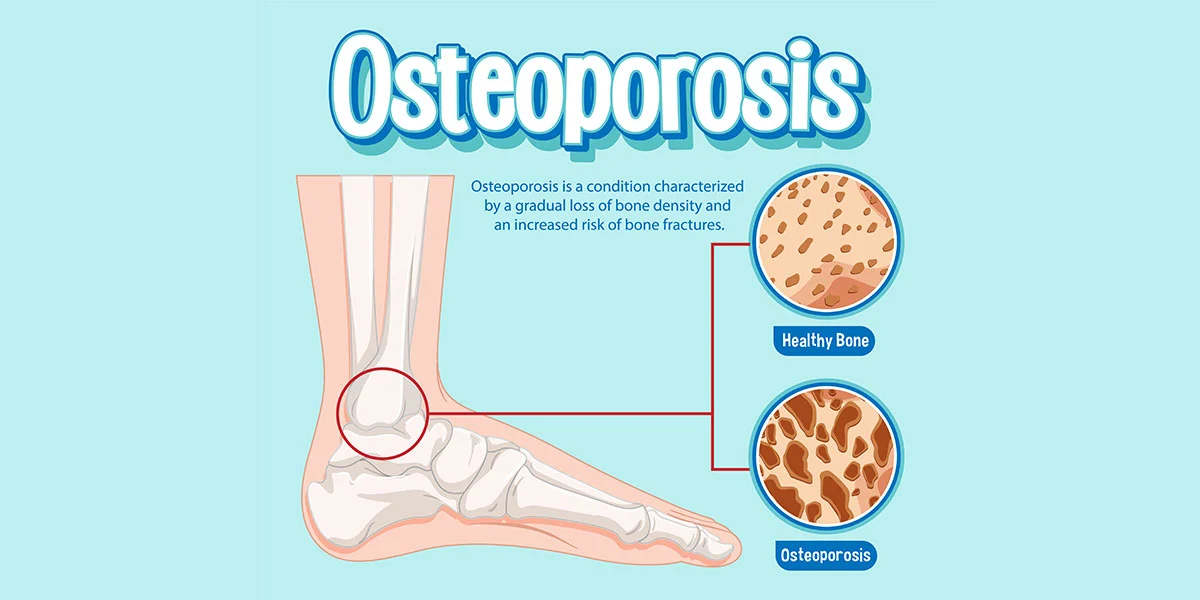
Osteoporosis: Symptoms, Causes, Tests & Treatment
Certainly! Here’s an overview of osteoporosis, including its symptoms, causes, diagnostic tests, and treatment options:
Symptoms of Osteoporosis:
Osteoporosis is often referred to as the “silent disease” because it doesn’t typically cause noticeable symptoms until a fracture occurs. Some of the symptoms and signs of osteoporosis include:
- Back pain, caused by fractured or collapsed vertebrae.
- Loss of height over time due to vertebral compression fractures.
- A stooped or hunched posture, also known as kyphosis.
- Increased susceptibility to fractures, especially in the wrist, hip, and spine, even from minor falls or bumps.
Causes of Osteoporosis:
The main cause of osteoporosis is an imbalance between bone formation and bone resorption. Factors that can contribute to the development of osteoporosis include:
- Aging: Bone mass naturally declines as people age, making older individuals more susceptible to osteoporosis.
- Hormonal Changes: Reduced estrogen levels in women after menopause and decreased testosterone levels in men can accelerate bone loss.
- Family History: A family history of osteoporosis may increase the risk of developing the condition.
- Low Calcium and Vitamin D Intake: Inadequate dietary intake of calcium and vitamin D can impair bone health.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of weight-bearing exercises and physical activity can weaken bones.
- Smoking: Smoking is associated with lower bone density and increased fracture risk.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Heavy alcohol consumption can negatively affect bone health.
- Certain Medications: Long-term use of glucocorticoids (steroids) and some other medications can contribute to bone loss.
Diagnostic Tests for Osteoporosis:
- Bone Density Test (DXA or DEXA): Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) is the most commonly used test to measure bone density at the hip and spine. It helps in diagnosing osteoporosis and assessing fracture risk.
- FRAX Score: The Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX) estimates the 10-year probability of major osteoporotic fractures based on clinical risk factors.
Treatment of Osteoporosis:
- Lifestyle Changes: Regular weight-bearing exercises, a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, quitting smoking, and reducing alcohol intake can help improve bone health.
- Medications: There are various medications available to slow bone loss, promote bone formation, and reduce fracture risk. Some common medications include bisphosphonates, denosumab, teriparatide, and selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs).
- Fall Prevention: Taking precautions to prevent falls can reduce the risk of fractures. This includes making home modifications, using assistive devices, and improving balance and strength through exercise.
- Monitoring: Regular bone density tests and follow-ups with healthcare providers are essential to monitor treatment effectiveness and adjust treatment plans as needed.
If you don’t like this article/post please share your feedback.