Infertility: Types, Symptoms, Causes & Remedies, Infertility is typically defined as the inability to conceive or carry a pregnancy to term after a year or more of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse. It can also refer to the inability to contribute to conception. Infertility can affect both men and women and may stem from various factors such as hormonal imbalances, reproductive system issues, age, genetic factors, lifestyle choices, or underlying medical conditions.
Types of Infertility
Infertility can manifest in various forms, and it’s often categorized based on its origins or causes.
Here are some types:
- Primary infertility: When a couple has never been able to conceive after at least one year of unprotected sex.
- Secondary infertility: Occurs when a couple has previously conceived (naturally or with assistance) but is struggling to conceive again.
- Male infertility: Refers to issues related to the male reproductive system that hinder conception. This might involve low sperm count, poor sperm motility, or structural problems.
- Female infertility: Relates to factors within the female reproductive system that impede conception. This can include issues such as ovulation disorders, blocked fallopian tubes, endometriosis, or hormonal imbalances.
- Unexplained infertility: When no identifiable cause for infertility can be found after thorough testing of both partners. This can be frustrating as there’s no specific reason found despite extensive evaluations.
- Lifestyle-induced infertility: Factors like smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, poor diet, stress, and certain medications can contribute to infertility in both men and women.
- Age-related infertility: As individuals age, fertility tends to decrease, especially for women. This is due to the natural decline in the quantity and quality of eggs.
- Medical or health-related infertility: Certain medical conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, sexually transmitted infections, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders can impact fertility.
Understanding the specific type of infertility a person or couple is facing can be crucial in determining the appropriate treatment or intervention methods. Consulting with a healthcare professional specializing in fertility can help in diagnosing and addressing these issues effectively.

Symptoms of Infertility
Infertility itself might not exhibit noticeable symptoms, but certain signs could indicate an underlying issue affecting fertility.
These signs can vary depending on the cause of infertility and may manifest differently in men and women:
Symptoms in Women:
- Irregular menstrual cycles: Abnormal or irregular periods might suggest ovulation issues.
- Painful periods: Severe menstrual cramps might be a sign of conditions like endometriosis.
- Hormonal fluctuations: Changes in hormone levels may cause symptoms like weight gain, hair growth, or skin changes.
- Painful intercourse: This might be indicative of conditions affecting the reproductive organs.
- Recurrent miscarriages: Experiencing multiple miscarriages might signal an underlying fertility issue.
Symptoms in Men:
- Changes in sexual function: Difficulty maintaining an erection or ejaculation issues might suggest problems with fertility.
Changes in testicle size or pain: Swelling, lumps, or pain in the testicles might indicate an issue. - Issues with ejaculation: Problems with ejaculation, low volume, or absence of ejaculate might be signs of infertility.
- Hormonal issues: Changes in hair growth, reduced libido, or other signs of hormonal imbalance might contribute to fertility problems.
Common Signs for Both: - Age-related concerns: As individuals age, fertility naturally declines.
- Underlying health conditions: Conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, or autoimmune diseases might impact fertility.
- Lifestyle factors: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, obesity, and stress can affect fertility in both men and women.
Keep in mind that while these symptoms could indicate potential fertility issues, some individuals might not experience any symptoms at all. If you suspect infertility or are having trouble conceiving, seeking guidance from a healthcare professional specializing in reproductive health or fertility can help in diagnosing and addressing any underlying concerns.
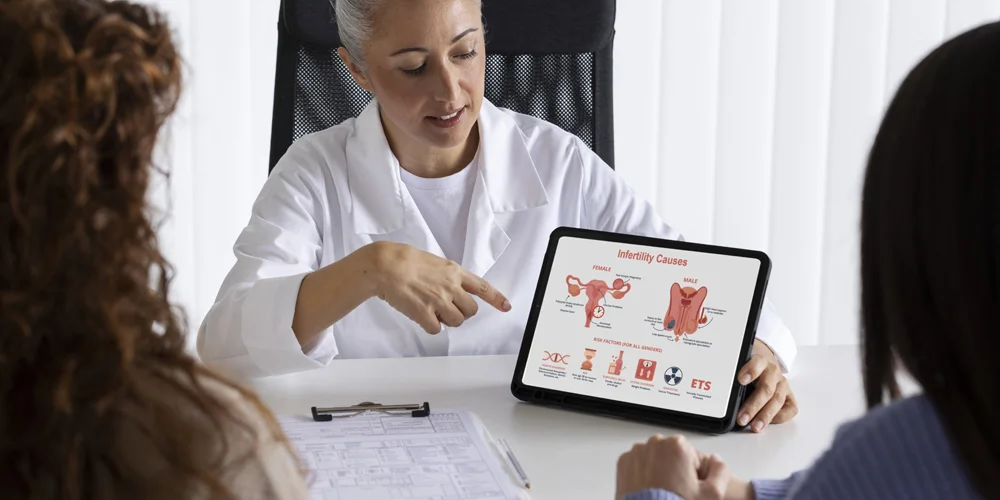
Causes of Infertility
Infertility can stem from various factors, impacting either men, women, or both partners.
Some common causes include:
Female Factors:
- Ovulation Disorders: Irregular or absent ovulation can hinder conception. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) often cause ovulation irregularities.
- Endometriosis: The presence of endometrial tissue outside the uterus can affect the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and other pelvic structures, leading to infertility.
- Fallopian Tube Damage or Blockage: Scarring, infections, or other issues in the fallopian tubes can prevent the egg from meeting the sperm.
- Uterine or Cervical Problems: Abnormalities in the uterus or cervix can impede implantation or the passage of sperm.
Age: As women age, the quantity and quality of eggs decline, reducing fertility.
Male Factors:
- Low Sperm Count or Quality: Issues with sperm count, motility, or morphology can affect fertility.
- Ejaculation Disorders: Problems with ejaculation, such as retrograde ejaculation (when semen enters the bladder instead of emerging through the penis), can impact fertility.
- Structural Issues: Blockages or abnormalities in the male reproductive tract can hinder the delivery of sperm.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Issues with hormone production or regulation can affect sperm production and function.
Other Factors Affecting Both Genders: - Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, drug use, obesity, and poor diet can influence fertility in both men and women.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Conditions like diabetes, thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and certain infections can affect fertility.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain toxins, chemicals, or radiation can impact fertility.
- Stress: High levels of stress can interfere with hormonal balance and reproductive function, affecting fertility.
Identifying the specific cause or causes of infertility often involves a comprehensive evaluation by healthcare professionals specializing in reproductive health. Treatment and interventions can vary widely depending on the underlying issues, and often a combination of medical, surgical, or assisted reproductive techniques may be utilized to address infertility.

Remedies of Infertility
The treatment for infertility depends on the underlying cause and can vary significantly from person to person.
Here are some common remedies or treatments:
Lifestyle Changes:
- Healthy Diet and Exercise: Maintaining a healthy weight and a balanced diet can positively impact fertility.
- Avoidance of Harmful Substances: Quitting smoking, reducing alcohol intake, and avoiding illicit drugs can improve fertility.
- Stress Management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, or counseling can help manage stress, which might affect fertility.
Medical Interventions:
- Medications: Hormonal treatments to regulate ovulation or enhance sperm production might be prescribed.
- Surgery: Corrective surgery for conditions like endometriosis, blocked fallopian tubes, or varicoceles (enlarged veins in the scrotum) may help.
Fertility Drugs and Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART): - Intrauterine Insemination (IUI): Sperm is directly inserted into the uterus during ovulation.
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): Fertilization occurs outside the body, where eggs and sperm are combined in a laboratory and then implanted into the uterus.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): A single sperm is injected directly into an egg to assist fertilization in cases of severe male infertility.
Alternative Therapies:
- Acupuncture: Some studies suggest it might improve fertility by reducing stress and improving blood flow to reproductive organs.
- Herbal Remedies: Some herbs are believed to positively impact fertility, but their effectiveness might vary, and caution is advised due to potential side effects and interactions.
Psychological Support:
- Counseling or Support Groups: Dealing with infertility can be emotionally challenging. Support from professionals or peers can be beneficial.
- Donor Options: Donor Sperm or Eggs: In cases where conception using one’s own gametes isn’t possible, donor options might be considered.
- Adoption: Adoption: For some individuals or couples, adoption might be a chosen path to parenthood.
It’s essential to seek guidance from healthcare professionals specializing in fertility to determine the most suitable treatment or combination of treatments based on individual circumstances and the specific causes of infertility. The choice of remedy often involves considering factors like age, health status, duration of infertility, personal preferences, and financial considerations.
Is infertility permanent?
Infertility isn’t always permanent. It depends on the underlying cause and various factors. For some individuals or couples, infertility might be temporary and treatable, while for others, it might be a permanent condition.
Treatable Infertility:
- Correctable Causes: Certain conditions causing infertility, such as hormonal imbalances, blocked fallopian tubes, or sperm quality issues, can sometimes be treated with medications, surgeries, or assisted reproductive technologies.
- Lifestyle Modifications: In cases where lifestyle factors contribute to infertility, changes in habits like quitting smoking, managing weight, or reducing stress can positively impact fertility.
Permanent Infertility:
- Irreversible Conditions: Some medical conditions or factors, such as advanced age, certain genetic conditions, severe damage to reproductive organs, or irreversible infertility issues, might lead to a permanent inability to conceive.
- Unexplained Infertility: In some cases, despite extensive testing, no identifiable cause for infertility is found. While this can be frustrating, it doesn’t necessarily mean permanent infertility, but the treatment path might be less clear.
Seeking guidance from fertility specialists or reproductive endocrinologists can help determine the specific cause of infertility and the chances of successful treatment. While advancements in reproductive medicine offer various options to address infertility, not all cases can be resolved, leading some individuals or couples to explore alternatives like adoption or embracing a child-free lifestyle.
It’s essential to discuss concerns about fertility with healthcare professionals who can provide personalized advice, explore treatment options, and offer support throughout the process.