Hair Loss, Types also known as alopecia, is a common condition that affects many people worldwide. It can occur in both men and women and can have various causes and patterns of presentation.
Types of Hair Loss:
There are several types of hair loss, also known as alopecia. Each type of hair loss has its own distinct characteristics and underlying causes.
Here are some common types of hair loss:
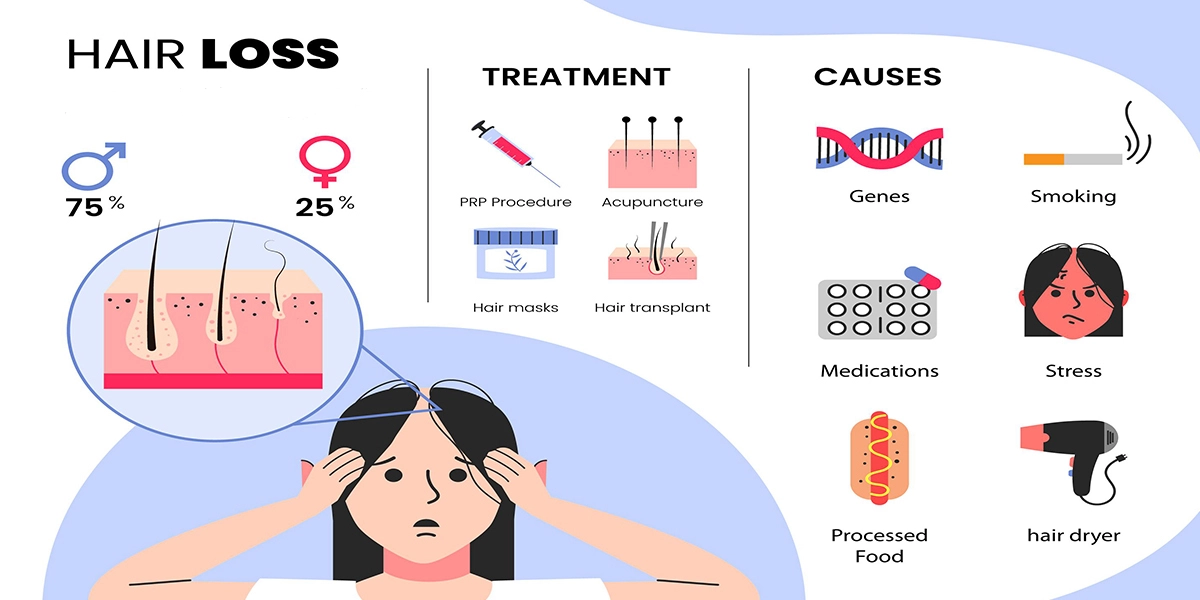
- Androgenetic Alopecia (Male/Female Pattern Baldness): This is the most common type of hair loss and is usually hereditary.
– In men, it often results in a receding hairline and thinning on the crown of the head.
– In women, it leads to diffuse thinning of the hair on the scalp without significant hairline recession. - Alopecia Areata: Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the hair follicles, leading to patchy hair loss.
– It can affect any hair-bearing area, including the scalp, eyebrows, and beard.
– In some cases, it may progress to complete baldness (alopecia totalis) or loss of all body hair (alopecia universalis). - Telogen Effluvium: Telogen effluvium is a temporary form of hair loss caused by a disturbance in the hair growth cycle.
– It is often triggered by factors such as stress, illness, hormonal changes, childbirth, or certain medications.
– Hair shedding is more diffuse and usually not concentrated in specific areas. - Traction Alopecia: Traction alopecia is hair loss caused by constant pulling or tension on the hair due to tight hairstyles like braids, ponytails, or hair extensions.
– It is more common in people who frequently style their hair in ways that stress the hair shafts. - Scarring Alopecia: Scarring alopecia results in permanent hair loss due to the destruction of hair follicles and replacement with scar tissue.
– It can be caused by various conditions, including inflammation, infections, or other skin disorders. - Anagen Effluvium: Anagen effluvium is rapid hair loss that affects the entire scalp and body.
– It is usually caused by exposure to chemicals or radiation, such as during cancer chemotherapy. - Alopecia Universalis: Alopecia universalis is a rare form of alopecia areata that leads to the loss of all body hair, including scalp hair, eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair.
- Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia: Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a type of scarring alopecia that primarily affects the frontal hairline and eyebrow area in postmenopausal women.
- Trichotillomania: Trichotillomania is a psychological disorder where individuals have an irresistible urge to pull out their hair, leading to patchy hair loss.
It’s important to note that the appropriate treatment for hair loss depends on the specific type and underlying cause. If you are experiencing hair loss, it’s essential to seek professional advice from a dermatologist or a hair specialist for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations.
Symtoms, for hair loss:
The symptoms of hair loss can vary depending on the type and underlying cause of the condition.
Here are some common symptoms associated with hair loss:
- Excessive Hair Shedding: Increased hair shedding, especially during combing, brushing, or washing the hair, is a common early symptom of hair loss.
- Thinning Hair: Gradual thinning of the hair on the scalp is a hallmark symptom of androgenetic alopecia (male or female pattern baldness).
- Receding Hairline: In men, a receding hairline, starting from the temples and moving backward, is a characteristic sign of male pattern baldness.
- Bald Patches: In conditions like alopecia areata, bald patches can appear on the scalp or other hair-bearing areas of the body.
- Reduced Hair Volume: People with hair loss may notice that their hair feels less dense or voluminous than before.
- Hair Breakage: Hair that appears frayed or damaged, with frequent breakage, can indicate hair loss due to excessive styling, chemical treatments, or other damaging practices.
- Itching or Irritation: Some types of hair loss can cause itching, redness, or irritation of the scalp.
- Scalp Visibility: As hair loss progresses, the scalp may become more visible through the thinning hair, especially when the hair is pulled back or in certain hairstyles.
- Hair Growth Changes: Changes in the rate of hair growth or the texture of new hair may be noticeable in some forms of hair loss.
- Patchy Eyebrows or Eyelashes: Hair loss conditions like alopecia areata can also affect the eyebrows and eyelashes, causing patchy loss in those areas.
- Stress or Emotional Distress: Hair loss can lead to emotional distress, anxiety, or lowered self-esteem in some individuals.
It’s important to remember that some degree of hair shedding is normal, and everyone’s hair goes through cycles of growth and shedding. However, if you are experiencing excessive or prolonged hair loss, or if you notice any concerning changes in your hair, it’s best to consult a medical professional. They can help determine the underlying cause of your hair loss and recommend appropriate treatments or lifestyle changes to address the issue effectively. Early intervention is essential for managing hair loss successfully.
Treatments for Hair Loss:
The treatment for hair loss depends on the underlying cause and the type of alopecia.
Here are some common treatments for different types of hair loss:
- Androgenetic Alopecia (Male/Female Pattern Baldness): Medications: Minoxidil (Rogaine) is an over-the-counter topical solution that can slow down hair loss and promote hair regrowth in both men and women. Finasteride (Propecia) is an oral prescription medication that is effective for male pattern baldness but not recommended for women of childbearing age due to potential pregnancy risks.
– Hair Transplant: For advanced cases of male or female pattern baldness, hair transplant surgery is an option. During the procedure, hair follicles are harvested from donor areas and transplanted to areas with thinning or no hair. - Alopecia Areata: Corticosteroids: Corticosteroid injections into the bald patches can help stimulate hair regrowth in alopecia areata.
– Topical Immunotherapy: A chemical is applied to the scalp to provoke an allergic reaction, which may encourage hair regrowth.
– Systemic Medications: For severe cases, medications that suppress the immune system (such as oral corticosteroids) may be prescribed. - Telogen Effluvium: Managing Underlying Causes: Addressing and treating the underlying triggers, such as reducing stress, improving nutrition, or managing medical conditions, can help hair regrowth.
– Minoxidil: In some cases, minoxidil may be prescribed to stimulate hair growth. - Traction Alopecia: Avoiding Tight Hairstyles: The first step is to stop using hairstyles that put excessive tension on the hair follicles. Allowing the hair to rest and recover can lead to regrowth in some cases.
- Scarring Alopecia: Scarring alopecia is challenging to treat, as the hair follicles are permanently damaged. In some cases, early intervention with anti-inflammatory medications may help slow the progression.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Addressing Nutritional Imbalances: Ensuring a balanced diet with adequate nutrients can promote overall hair health.
- Medication-Induced Hair Loss: Sometimes, adjusting the medication dosage or switching to an alternative medication can help stop hair loss.
– In chemotherapy-induced hair loss, hair typically regrows once the treatment is completed. - Laser Therapy: Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) devices are available for home use or in clinics, and they are thought to stimulate hair growth by improving blood circulation in the scalp.
It’s essential to consult a dermatologist or a hair specialist for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment recommendations. The effectiveness of treatments can vary from person to person, and early intervention often provides the best results. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and using gentle hair care practices can help support overall hair health.

When to see a doctor for hair loss ?
If you are experiencing hair loss and it is causing you concern or distress, it is generally a good idea to see a doctor or a dermatologist.
Here are some specific situations when you should consider seeking medical advice for hair loss:
- Sudden or Severe Hair Loss: If you notice a sudden and significant increase in hair shedding or hair loss, it’s essential to consult a doctor to determine the underlying cause.
- Rapidly Receding Hairline: Men who notice a receding hairline or women experiencing noticeable thinning in the frontal area of the scalp should seek medical evaluation.
- Patchy Hair Loss: If you have areas of bald patches or specific spots where hair is thinning, it could be a sign of alopecia areata or other conditions that require medical attention.
- Family History of Hair Loss: If you have a family history of androgenetic alopecia (male or female pattern baldness), and you are starting to notice similar signs of hair loss, consider discussing it with a doctor to explore potential preventive measures or treatments.
- Hair Loss with Itching, Redness, or Scaling: If your hair loss is accompanied by symptoms such as itching, redness, scaling, or pain, it could be due to an underlying scalp condition that needs medical evaluation.
- Sudden Changes in Hair Growth: If you notice a sudden increase in hair growth in areas where it is not typical, it could be a sign of an underlying hormonal or medical condition.
- Hair Loss after Medical Treatment: If you’ve recently undergone medical treatments like chemotherapy, and you are experiencing hair loss, it’s essential to talk to your healthcare provider about managing this side effect.
- Emotional Distress: Hair loss can have a significant emotional impact on individuals. If you are feeling distressed or anxious about your hair loss, seeking professional advice can help address your concerns and explore treatment options.
Remember that some degree of hair shedding is normal, and our hair naturally goes through cycles of growth and shedding. However, if you are experiencing excessive hair loss or notice any concerning changes in your hair, it’s best to consult a medical professional. They can help identify the cause of your hair loss and recommend appropriate treatments or lifestyle changes to address the issue effectively.
What are the cycles of hair growth?
The hair growth cycle consists of three main phases, and each hair on your scalp goes through these phases independently. Understanding the hair growth cycle is essential to comprehend how hair grows, sheds, and regenerates.
The three phases of the hair growth cycle are:
- Anagen Phase (Growth Phase): The anagen phase is the active growth phase of the hair follicle.
– During this phase, the hair bulb at the base of the hair follicle divides rapidly, and new hair cells are formed, pushing the older ones upward.
– The hair grows longer during this phase, and its length can vary depending on genetics and individual factors.
– The anagen phase typically lasts between two to seven years for scalp hairs. - Catagen Phase (Transition Phase): The catagen phase is a transitional phase that marks the end of the active growth phase.
– During this short phase, the hair follicle shrinks and detaches from the blood supply, effectively stopping hair growth.
– The catagen phase usually lasts for about two to three weeks. - Telogen Phase (Resting Phase): The telogen phase is the resting phase of the hair follicle.
– During this phase, the hair follicle remains dormant, and the hair is no longer growing.
– The hair is held in place by the follicle while a new hair starts to grow underneath it.
– The telogen phase lasts for about two to four months.
– After the telogen phase, the old hair is shed, and the new hair starts to grow, initiating a new anagen phase.
It’s essential to note that not all hairs on the scalp are in the same phase at the same time. At any given moment, some hairs are actively growing (anagen), some are transitioning (catagen), and others are resting (telogen). This cycling process allows the hair follicles to continuously renew themselves and replace old hairs with new ones.
On average, about 85-90% of scalp hairs are in the anagen phase, 1-2% are in the catagen phase, and 10-15% are in the telogen phase at any given time. Various factors, including genetics, age, hormones, and overall health, can influence the duration of each phase and, consequently, affect individual hair growth patterns.
Which woman are likely to experience hair loss?
Hair loss in women can occur due to various factors and conditions. While it is more common in men, women can also experience hair loss. Some women are more likely to experience hair loss than others due to certain risk factors and underlying causes.
Here are some factors that can increase the likelihood of hair loss in women:
- Family History: A strong family history of hair loss, especially if the mother, father, or other close relatives experienced hair thinning or pattern baldness, can increase the risk of hair loss in women.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or while using hormonal contraceptives, can lead to temporary hair shedding or hair loss.
- Androgenetic Alopecia: This is the female pattern hair loss that is caused by genetic and hormonal factors. Women with a family history of androgenetic alopecia are more likely to experience this type of hair loss.
- Age: Hair thinning and hair loss tend to increase with age, especially after menopause.
- Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, and other hormonal imbalances, can contribute to hair loss in women.
- Stress: High levels of emotional or physical stress can lead to temporary hair loss, known as telogen effluvium.
- Hairstyles: Frequent use of tight hairstyles that pull on the hair, such as braids, ponytails, or extensions, can cause traction alopecia.
- Hair Treatments: Excessive use of harsh hair treatments, chemical dyes, perms, or straighteners can damage the hair and lead to hair breakage or hair loss.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Poor nutrition and certain vitamin or mineral deficiencies can impact hair health and contribute to hair loss.
- Medications: Some medications, such as certain antidepressants, anticoagulants, and chemotherapy drugs, can cause hair loss as a side effect.
- Trichotillomania: This is a psychological condition where individuals have an irresistible urge to pull out their hair, leading to patchy hair loss.
It’s important to note that the specific cause of hair loss in women can vary significantly from person to person. If you are experiencing hair loss or noticeable hair thinning, it’s essential to seek medical advice from a dermatologist or a healthcare professional. They can evaluate your individual situation, identify the underlying cause, and recommend appropriate treatments or lifestyle changes to manage or reverse the hair loss.
Read this Article Also: Sudden Hair Loss in Women | Prevention by Essential Vitamins
If you don’t like this article/post please share your feedback.