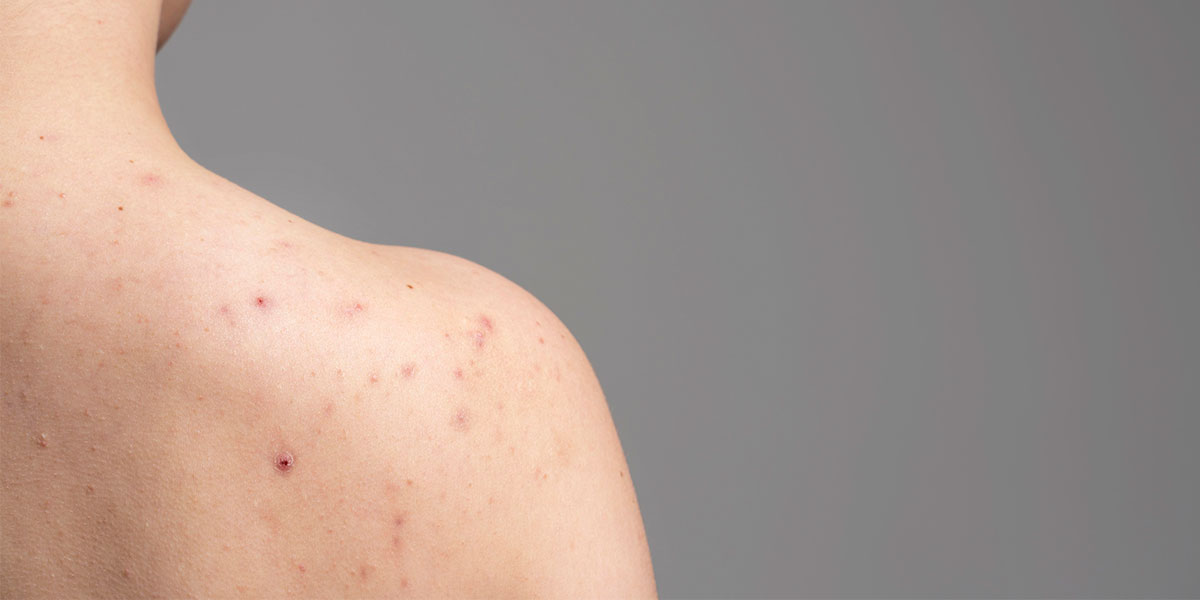
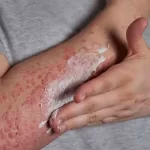
Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). It is a common childhood disease but can affect people of all ages. Chickenpox is characterized by a distinctive rash of itchy, red, and fluid-filled blisters that appear on the skin.
Here are some key points about chickenpox:
- Transmission: Chickenpox spreads through direct contact with the fluid from the blisters or through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It is highly contagious and can also be contracted by being in close proximity to an infected person.
- Incubation period: The incubation period for chickenpox is usually about 10 to 21 days after exposure. It means that someone who has been exposed to the virus may not show symptoms immediately.
- Symptoms: The symptoms of chickenpox typically start with a mild fever, headache, and feeling unwell. After a day or two, the characteristic rash appears, initially as small red spots that quickly progress into itchy blisters. The rash may cover the entire body, including the scalp, mouth, and genital area.
- Itching: The rash can be extremely itchy, which can be uncomfortable for the person affected, especially children. Scratching the blisters can lead to complications, such as bacterial skin infections or scarring.
- Contagiousness: A person with chickenpox is contagious from one to two days before the rash appears until all the blisters have crusted over. This period usually lasts about 5 to 7 days.
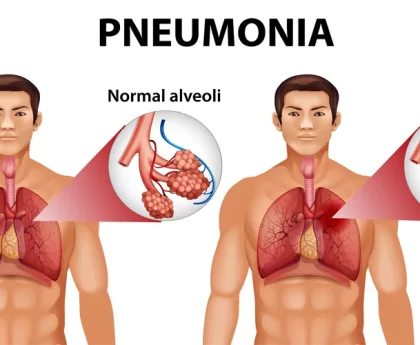
- Complications: In most cases, chickenpox is a mild and self-limiting illness. However, it can lead to complications, especially in certain high-risk groups such as infants, pregnant women, people with weakened immune systems, and adults. Common complications include bacterial skin infections, pneumonia, and encephalitis (inflammation of the brain).
- Vaccination: Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent chickenpox. The varicella vaccine is routinely given to children in many countries and has significantly reduced the incidence of the disease. In some regions, a two-dose vaccination schedule is recommended.
- Chickenpox and Shingles: After a person recovers from chickenpox, the varicella-zoster virus remains dormant in the nervous system. Later in life, the virus may reactivate and cause a condition called shingles (herpes zoster), which is characterized by a painful rash with blisters. Shingles can occur in anyone who has previously had chickenpox.
If you suspect you or someone you know has chickenpox, it’s important to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and management, especially for those at higher risk of complications. Avoiding close contact with infected individuals and maintaining good hygiene practices can help reduce the spread of the virus.
Causes of Chickenpox
The virus is highly contagious and primarily spreads through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs or sneezes. It can also spread through direct contact with the fluid from the blisters on the skin of an infected person.
Here’s how the transmission of the varicella-zoster virus occurs:
- Respiratory droplets: When an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks, tiny droplets containing the virus are released into the air. If a person who is not immune to chickenpox inhales these infected droplets, they can become infected.
- Direct contact: The virus can also spread through direct contact with an infected person’s skin lesions. If a person touches the fluid-filled blisters of someone with chickenpox and then touches their own mouth, nose, or eyes, they can become infected.
- Airborne particles: The virus can remain active in the air for a short period, so an individual may also contract chickenpox by being in close proximity to an infected person.
Once a person becomes infected with the varicella-zoster virus, it can take between 10 to 21 days for symptoms to appear. During this incubation period, the virus begins to replicate in the body and travel to the skin, leading to the characteristic rash and other symptoms of chickenpox.
It’s important to note that people who have had chickenpox once typically develop immunity to the virus, meaning they are unlikely to get infected again. However, as the virus remains dormant in the nerve cells, it can reactivate later in life and cause shingles (herpes zoster) in some individuals. Shingles is a painful rash that occurs in individuals who have previously had chickenpox.
Symptoms of Chickenpox
Chickenpox is characterized by a set of distinctive symptoms, which typically develop within 10 to 21 days after exposure to the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). The symptoms of chickenpox can vary in severity, and they generally follow a specific progression.
Here are the common symptoms:
- Fever: Chickenpox often begins with a mild to moderate fever, which may last for a few days.
- Headache: Headaches can be one of the early symptoms experienced by some individuals with chickenpox.
- Loss of Appetite: Many people infected with the virus may experience a loss of appetite.
- Fatigue and General Discomfort: Feeling generally unwell, tired, and irritable is common in the early stages of chickenpox.
- Rash: A characteristic rash is a hallmark symptom of chickenpox. The rash typically starts as small, red spots, which then develop into itchy, fluid-filled blisters over time. The rash can appear on the face, trunk, and limbs and may also spread to the scalp, mouth, and genital area.
- Itching: The rash is highly itchy, and scratching it can lead to skin infections and potential scarring.
- Blisters and Crusts: The fluid-filled blisters eventually burst and form scabs or crusts. New blisters may continue to appear for several days.
- Contagiousness: A person with chickenpox is contagious from one to two days before the rash appears until all the blisters have crusted over.
- Distribution: The rash tends to be more concentrated on the trunk and face, with fewer blisters on the extremities.
It’s essential to note that the severity of chickenpox can vary from person to person. In some cases, especially in healthy children, it may be a relatively mild illness. However, in certain high-risk groups, such as infants, pregnant women, and people with weakened immune systems, chickenpox can lead to more severe complications. These complications can include bacterial skin infections, pneumonia, encephalitis (inflammation of the brain), and, rarely, death.
If you suspect you or someone you know has chickenpox, it is crucial to seek medical advice for proper diagnosis and management, especially for individuals at higher risk of complications. Additionally, to prevent the spread of the virus, infected individuals should avoid close contact with others, especially those who have not had chickenpox or received the varicella vaccine.

Treatment of Chickenpox:
- Symptomatic Relief: Chickenpox is usually a self-limiting condition that resolves on its own over time. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms such as fever and itching. Over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used to reduce fever and discomfort. It is important to avoid aspirin in children and teenagers with chickenpox due to the risk of developing Reye’s syndrome, a rare but severe condition.
- Itch Relief: Calamine lotion or antihistamine creams can help alleviate the itching associated with the chickenpox rash. Antihistamines taken orally may also be prescribed to reduce itching and improve sleep.
- Maintaining Good Hygiene: Keeping the skin clean and the nails short can help prevent secondary bacterial infections caused by scratching the itchy blisters.
- Comfort Measures: Drinking plenty of fluids and staying well-hydrated is essential, especially if the individual has a fever.
- Isolation: Since chickenpox is highly contagious, infected individuals should avoid close contact with others, especially those who have never had chickenpox or been vaccinated against it.
- Antiviral Medications: In some cases, antiviral medications such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir may be prescribed, especially for individuals at high risk of complications. These medications can help reduce the severity and duration of the illness if started early in the course of the infection.
Prevention of Chickenpox:
- Vaccination: The most effective way to prevent chickenpox is through vaccination. The varicella vaccine is recommended for all children and adults who have not had chickenpox. The vaccine is typically given in two doses to provide long-lasting immunity. Vaccination not only prevents chickenpox but also reduces the severity of the disease if a vaccinated person does get infected.
- Avoiding Contact: Since chickenpox is highly contagious, avoiding close contact with infected individuals is crucial to prevent transmission.
- Post-Exposure Prophylaxis: If someone has been exposed to chickenpox and is at high risk of severe illness (e.g., pregnant women, immunocompromised individuals), varicella-zoster immune globulin (VZIG) may be administered to reduce the severity of the infection.
- Vaccination of Close Contacts: If a person is not immune to chickenpox and has been in contact with an infected individual, vaccination within a specific timeframe can help prevent or reduce the severity of the illness.
It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for advice on vaccination and management, especially for individuals at higher risk of complications from chickenpox. Additionally, following good hygiene practices and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can contribute to overall immunity and well-being.
चेचक के लक्षण, कारण और घरेलू इलाज
चेचक (Chickenpox) एक वायरल संक्रामक बीमारी है जिसे वेरिसेला-जोस्टर वायरस (Varicella-Zoster Virus, VZV) से प्रकारित होता है। यह बीमारी सामान्यतः बचपन की उम्र के बच्चों में होती है, लेकिन यह सभी उम्र के लोगों को प्रभावित कर सकती है। निम्नलिखित हैं चेचक के लक्षण, कारण और घरेलू इलाज के बारे में जानकारी:
चेचक के लक्षण:
- बुखार: चेचक के लक्षणों में से एक बुखार का होना शामिल होता है। इस बुखार की तापमान आमतौर पर मध्यम से गंभीर होती है।
- सिरदर्द: कुछ लोगों को चेचक के शुरुआती चरण में सिरदर्द होता है।
- भूख की कमी: चेचक के ग्रस्त व्यक्तियों को भूख की कमी हो सकती है।
- थकान: चेचक के प्रारंभिक चरण में व्यक्ति थकावट महसूस कर सकता है और चिढ़चिढ़ाहट भी हो सकती है।
- खुजली: चेचक के लक्षणों में एक मुख्य लक्षण है खुजली। राशि आमतौर पर चेहरे, ट्रंक, और अंगों पर होती है और धीरे-धीरे पानी भरे दाने बन जाते हैं जो इच्छानुसार खुजलते हैं।
- दानों का रंग बदलना: चेचक के दाने आमतौर पर शुरुआत में लाल या गुलाबी होते हैं, और धीरे-धीरे वे कोई चमकदार ग्यारहरंग के बड़े दाने बन जाते हैं, जो बाद में धूप देने से खराब हो जाते हैं और फिर सूखकर छाज़ के समान हो जाते हैं।
चेचक के कारण:
चेचक वायरस (VZV) के संपर्क में आने से चेचक होती है। निम्नलिखित तत्व इस वायरस के प्रसार का कारण बन सकते हैं:
- संपर्क: दिनों वायरस से संपर्क में आने पर इंफेक्शन हो सकता है। यह संपर्क बुखारी व्यक्ति के साथ सीधा संपर्क या वायुमंडल के माध्यम से भी हो सकता है।
- संक्रमणित वस्त्रों या सामग्री का संपर्क: अगर संक्रमित व्यक्ति के इलाज के समय उसके वस्त्रों, तौलियों, या खिलौनों का दूसरों के साथ संपर्क हो तो भी वायरस आसानी से फैल सकता है।
- गर्मियों में अधिक प्रसार: चेचक के मामूले होने का कारण गर्मियों में वायरस के प्रसार की बढ़ती घटना है।
चेचक का घरेलू इलाज:
- ताज़े पानी से नहाना: राशि खुजली की वजह से और भी ज्यादा इच्छुक होती है, इसलिए नहाने से पहले और बाद में ध्यानपूर्वक धो लेना चाहिए। ताज़े गरम पानी से नहाने से खुजली में राहत मिलती है।
- केसर का उपयोग: बच्चों को चेचक के दौरान गर्म दूध में थोड़ा सा केसर मिलाकर देना भी लाभप्रद हो सकता है।
- खैरा: खैरा (neem) के पत्ते के पेस्ट को राशि पर लगाने से खुजली कम हो सकती है और यह एक प्राकृतिक उपाय है।
- गुलाबी पानी: राशि पर गुलाबी पानी छिड़कने से भी राहत मिलती है।
कृपया ध्यान दें कि यह सिर्फ घरेलू उपाय हैं। यदि आपको या आपके परिवार के किसी सदस्य को चेचक के लक्षण हों तो आपको तत्काल चिकित्सक की सलाह लेनी चाहिए। चेचक गंभीर समस्या हो सकती है और उचित चिकित्सा देखभाल जरूरी है।
Read these Articles also:
- Turmeric for Acne: The Ultimate Guide to Clear and Glowing Skin
- Tallow for Skin Care: Benefits, Side Effects and How to Use
- Neem Benefits for Skin | Younger Glowing Skin and Hair
- Olive Oil Massage | Benefits and Side Effects for Male and Female
If you don’t like this article/post please share your feedback.