Junk food refers to highly processed or unhealthy foods that are typically low in nutritional value and high in calories, unhealthy fats, sugar, and salt. These foods are often convenient, easily accessible, and have a pleasant taste, but they lack essential nutrients needed for overall health and well-being.
Common examples of junk food include:
- Fast Food: Burgers, fries, pizzas, hot dogs, and other items from fast-food restaurants.
- Sugary Snacks: Candies, chocolates, pastries, doughnuts, and sugary cereals.
- Sugary Drinks: Soda, energy drinks, fruit juices with added sugars.
- Chips and Snack Foods: Potato chips, corn chips, and other packaged snacks high in unhealthy fats and sodium.
- Processed Foods: Ready-to-eat meals, microwave dinners, and heavily processed convenience foods.
- Deep-Fried Foods: Fried chicken, onion rings, and other foods with high oil content.
- Sweetened Breakfast Cereals: Cereals with high sugar content and low nutritional value.
Consuming junk food regularly can lead to various health issues, including obesity, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and other chronic conditions. It is crucial to limit the intake of junk food and focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to promote good health and well-rounded nutrition.
The Impacts of Junk Food on Health
Junk food can have significant negative impacts on health due to its poor nutritional quality and high levels of unhealthy components.
Some of the key health impacts of consuming junk food regularly include:
- Obesity: Junk food is often calorie-dense and low in essential nutrients. Regularly consuming these foods can lead to weight gain and obesity, as excess calories are stored as body fat.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Diets high in sugary and processed foods can contribute to insulin resistance and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Heart Disease: Junk food is typically high in unhealthy fats, trans fats, and sodium, which can raise blood pressure and cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Digestive Issues: The low fiber content in junk food can lead to digestive problems like constipation and irregular bowel movements.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Junk food lacks essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients necessary for proper body function. A diet lacking in key nutrients can lead to deficiencies and related health issues.
- Energy and Mood Swings: Junk food can cause rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels, leading to feelings of fatigue and mood swings.
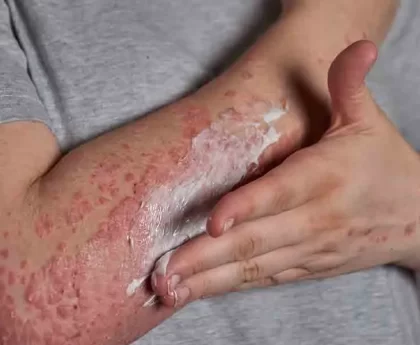
- Dental Problems: Sugary and acidic junk foods contribute to tooth decay and dental cavities.
- Increased Risk of Chronic Diseases: Long-term consumption of junk food is associated with an increased risk of chronic conditions such as certain types of cancer, metabolic syndrome, and fatty liver disease.
- Cognitive Impairment: Some studies suggest that a diet high in junk food may negatively impact cognitive function and memory.
- Addictive Behavior: The combination of sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats in junk food can trigger addictive-like eating patterns, making it challenging to resist cravings and leading to overconsumption.
It’s important to note that an occasional indulgence in junk food is generally not harmful for most people, but regular and excessive consumption can lead to serious health issues. To maintain good health, it’s essential to focus on a balanced diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods and to limit the intake of junk food and sugary beverages. Making healthier food choices can have a positive impact on overall well-being and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Advantages of Healthy Foods
Healthy foods offer numerous advantages that contribute to overall well-being and a better quality of life.
Some of the key advantages of consuming healthy foods include:
- Nutrient-Rich: Healthy foods are packed with essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, fiber, antioxidants, and phytochemicals, which are crucial for proper body function and maintaining optimal health.
- Weight Management: A balanced diet consisting of healthy foods can help in managing body weight, as they are generally lower in calories and higher in nutrients, keeping you feeling fuller for longer.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, certain cancers, and hypertension.
- Improved Digestion: High-fiber foods promote healthy digestion and regular bowel movements, reducing the risk of constipation and other digestive issues.
- Heart Health: Healthy foods can positively influence cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and blood sugar, supporting cardiovascular health.
- Enhanced Energy Levels: Nutrient-dense foods provide a steady source of energy, reducing energy crashes associated with processed and sugary foods.
- Boosted Immune System: The vitamins and minerals found in healthy foods support a robust immune system, helping the body defend against infections and illnesses.
- Better Cognitive Function: Certain nutrients in healthy foods, such as omega-3 fatty acids, have been linked to improved brain health, memory, and cognitive function.
- Improved Mood: Some studies suggest that a balanced diet can positively impact mood and reduce the risk of depression and anxiety.
- Healthy Skin, Hair, and Nails: Nutrient-rich foods contribute to healthy skin, hair, and nails, promoting a radiant appearance.
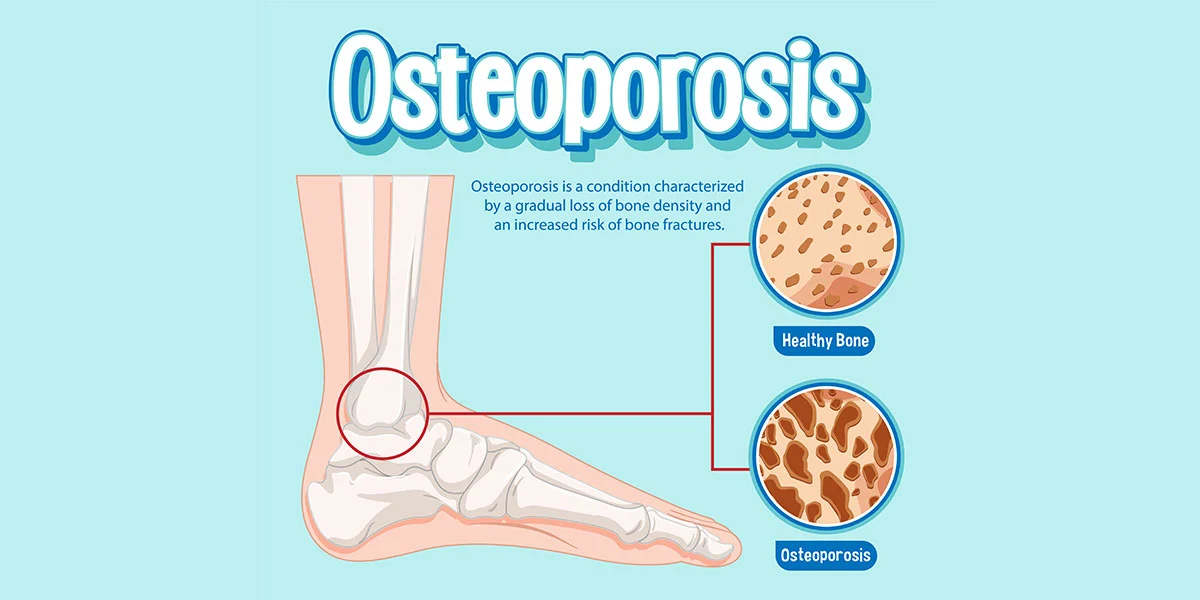
- Bone Health: Foods rich in calcium, vitamin D, and other bone-supporting nutrients can help maintain strong and healthy bones.
- Longevity: Adopting a healthy diet has been associated with a longer and healthier lifespan.
- Positive Eating Habits: Consuming healthy foods encourages better eating habits, making it easier to maintain a balanced diet over the long term.
- Sustainable Lifestyle: A diet focused on whole, plant-based foods can have a lower environmental impact compared to diets reliant on processed and animal-based products.
Overall, incorporating a wide variety of nutritious foods into your diet can have numerous positive effects on your physical and mental well-being, helping you lead a healthier and more fulfilling life.
What are the Long-Term Impacts of Junk Foods?
The long-term consumption of junk foods can have serious and detrimental effects on overall health.
Some of the key long-term impacts of regularly consuming junk foods include:
- Obesity: Junk foods are often high in calories, unhealthy fats, and sugars. Consistently eating these calorie-dense foods can lead to weight gain and obesity, increasing the risk of various health problems.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A diet high in sugary and processed foods can contribute to insulin resistance, which may lead to the development of type 2 diabetes over time.
- Heart Disease: Junk foods that are high in unhealthy fats, trans fats, and sodium can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels and high blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Metabolic Syndrome: Long-term consumption of junk foods can contribute to metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions that include high blood pressure, high blood sugar, excess body fat, and abnormal cholesterol levels.
- Gastrointestinal Issues: A diet high in processed and fatty foods can lead to gastrointestinal problems such as acid reflux, indigestion, and chronic inflammation of the digestive tract.
- Chronic Inflammation: Junk foods can trigger chronic inflammation in the body, which has been linked to various chronic diseases, including cancer, heart disease, and autoimmune disorders.
- Liver Damage: Regular consumption of sugary and fatty foods can contribute to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition where excess fat accumulates in the liver.
- Dental Problems: Sugary junk foods contribute to tooth decay and dental cavities, especially when consumed frequently without proper oral hygiene.
- Weakened Immune System: A diet lacking in essential nutrients can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
- Cognitive Decline: Some research suggests that a diet high in junk foods may be linked to cognitive decline and an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
- Reduced Bone Health: Junk foods often lack essential nutrients for bone health, which can lead to weakened bones and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
- Addictive Eating Patterns: The combination of sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats in junk foods can trigger addictive-like eating patterns, making it difficult for individuals to control their intake and leading to overeating.
It’s crucial to be mindful of the long-term impacts of junk foods and prioritize a balanced diet rich in whole, unprocessed foods. By making healthier food choices, individuals can reduce the risk of chronic diseases, improve overall health, and enhance their quality of life in the long run.
What are the Major Harmful Effects of Junk Food?
Junk food can have several major harmful effects on health due to its poor nutritional quality and high levels of unhealthy components.
Some of the major harmful effects of consuming junk food include:
- Obesity: Junk foods are often calorie-dense and lacking in essential nutrients. Regularly consuming these foods can lead to weight gain and obesity, which increases the risk of various health issues like type 2 diabetes, heart disease, and joint problems.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Diets high in sugary and processed foods can lead to insulin resistance and an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Cardiovascular Problems: Junk food is typically high in unhealthy fats, trans fats, and sodium, which can raise blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Digestive Issues: The low fiber content in junk food can lead to digestive problems like constipation and irregular bowel movements.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Junk food lacks essential vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients needed for proper body function, leading to nutritional deficiencies and related health issues.
- Weakened Immune System: A diet high in junk food can weaken the immune system, making the body more susceptible to infections and illnesses.
- Liver Damage: Regular consumption of sugary and fatty foods can contribute to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), a condition where excess fat accumulates in the liver.
- Dental Problems: Sugary junk foods contribute to tooth decay and dental cavities, especially when consumed frequently without proper oral hygiene.
- Mental Health Issues: Some studies suggest that diets high in junk food may be linked to an increased risk of depression and anxiety.
- Addictive Eating Patterns: The combination of sugar, salt, and unhealthy fats in junk foods can trigger addictive-like eating patterns, making it difficult for individuals to control their intake and leading to overeating.
- Cognitive Decline: Research indicates that diets high in junk foods may be associated with cognitive decline and an increased risk of neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
- Bone Health Issues: Junk foods often lack essential nutrients for bone health, which can lead to weakened bones and an increased risk of osteoporosis.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Some studies suggest that excessive consumption of junk food may lead to hormonal imbalances, which can have wide-ranging effects on health.
It’s important to be aware of the harmful effects of junk food and make healthier dietary choices. Reducing the intake of junk food and focusing on a balanced diet rich in whole, nutrient-dense foods can help promote better health and well-being in the long term.
What are the straight & simple Ways of eating Less Unhealthy Food?
Eating less unhealthy food can be achieved through simple strategies that promote healthier eating habits.
Here are some straightforward tips to help you reduce your intake of unhealthy foods:
- Plan Your Meals: Prepare a weekly meal plan with nutritious recipes and make a shopping list accordingly. Having a plan in place reduces the likelihood of impulsive, unhealthy food choices.
- Eat Mindfully: Pay attention to your eating habits, and avoid distractions like television or smartphones while eating. Eating mindfully can help you recognize when you’re full and prevent overeating.
- Practice Portion Control: Serve smaller portions of unhealthy foods or opt for a smaller plate. This way, you can satisfy your cravings without consuming excessive calories.
- Stock Healthy Snacks: Keep a supply of healthier snack options, such as fruits, nuts, yogurt, or cut vegetables, readily available. This makes it easier to resist reaching for unhealthy snacks.
- Limit Processed Foods: Minimize your intake of highly processed foods, which are often high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and sodium. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible.
- Drink Water: Sometimes, we mistake thirst for hunger. Stay hydrated by drinking enough water throughout the day, as it can help reduce unnecessary snacking.
- Avoid Sugary Beverages: Cut back on sugary sodas, energy drinks, and fruit juices with added sugars. Instead, choose water, herbal teas, or infused water for a healthier alternative.
- Read Labels: Pay attention to the nutritional information on food labels. Look for items with lower amounts of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium.
- Cook at Home: Prepare your meals at home as much as possible. This gives you control over the ingredients and cooking methods, ensuring healthier choices.
- Be Wary of Emotional Eating: Recognize emotional triggers that lead to unhealthy eating habits. Find alternative ways to cope with emotions, such as taking a walk, practicing mindfulness, or engaging in a hobby.
- Allow Occasional Treats: Depriving yourself completely of your favorite unhealthy foods can lead to binge eating. Allow yourself occasional treats in moderation to maintain balance and satisfaction.
- Eat More Fiber-Rich Foods: Foods high in fiber, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help you feel full and satisfied, reducing cravings for unhealthy snacks.
- Don’t Skip Meals: Skipping meals can lead to overeating later. Stick to regular mealtimes to maintain stable energy levels and prevent excessive hunger.
Remember that adopting healthier eating habits is a gradual process, and it’s okay to have occasional indulgences. By making small, sustainable changes to your diet, you can gradually reduce your consumption of unhealthy foods and improve your overall health and well-being.
Why Is Healthy Food Better Than Junk Food?
Healthy food is better than junk food for several reasons, primarily due to its positive impact on overall health and well-being.
Here are some key reasons why healthy food is a superior choice:
- Nutritional Value: Healthy foods are rich in essential nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, fiber, and healthy fats. These nutrients are vital for various bodily functions and support overall health.
- Weight Management: Healthy foods are generally lower in calories and higher in nutrients, making them a better option for weight management and maintaining a healthy body weight.
- Reduced Risk of Chronic Diseases: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is associated with a lower risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and certain types of cancer.
- Improved Digestion: High-fiber foods in a healthy diet promote healthy digestion and regular bowel movements, reducing the risk of gastrointestinal problems.
- Heart Health: Healthy foods can positively influence cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and blood sugar, supporting cardiovascular health.
- Enhanced Energy Levels: Nutrient-dense foods provide a steady source of energy, reducing energy crashes associated with processed and sugary foods.
- Strong Immune System: The vitamins and minerals found in healthy foods support a robust immune system, helping the body defend against infections and illnesses.
- Mental Health Benefits: A balanced diet has been linked to better mental health, improved mood, and reduced risk of depression and anxiety.
- Better Dental Health: Healthy foods contribute to better dental health by reducing the risk of tooth decay and gum disease.
- Positive Impact on Skin and Hair: Nutrient-rich foods support healthy skin, hair, and nails, promoting a radiant appearance.
- Improved Cognitive Function: Certain nutrients in healthy foods, such as omega-3 fatty acids, have been linked to improved brain health, memory, and cognitive function.
- Sustainable Lifestyle: A diet focused on whole, plant-based foods can have a lower environmental impact compared to diets reliant on processed and animal-based products.
- Positive Eating Habits: Consuming healthy foods encourages better eating habits, making it easier to maintain a balanced diet over the long term.
- Long-Term Health Benefits: Adopting a healthy diet can lead to a longer and healthier lifespan, with fewer health complications in later years.
In contrast, junk food offers little nutritional value, tends to be high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and sodium, and can contribute to numerous health problems. While occasional indulgence in junk food is generally acceptable, prioritizing healthy food choices provides a more sustainable and beneficial approach to nourishing your body and maintaining good health.
Read this Article Also
If you don’t like this article/post please share your feedback.