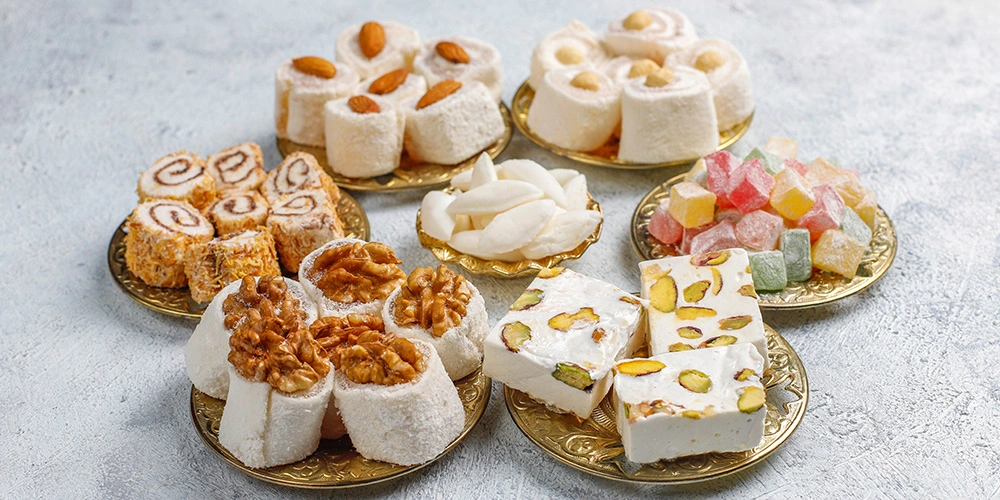
Indian Delicious Sweets: are a wide variety of confections, desserts, and sugary delicacies that are an integral part of Indian cuisine and culture. These sweets come in various forms, flavors, and textures, and they are enjoyed throughout the country on various occasions, celebrations, and festivals.
Definition of Indian Sweets
Indian delicious sweets are characterized by their use of ingredients such as milk, ghee (clarified butter), sugar, nuts, aromatic spices like cardamom and saffron, and sometimes fruits. They come in various forms, including soft and moist, crumbly, syrup-soaked, and more, offering a delightful array of tastes and textures.
These sweets are not only about taste but also about cultural significance, as they are often exchanged during festivals, shared with guests, and used in rituals. They showcase the diversity of Indian cuisine and reflect the traditions and culinary artistry of different regions within the country.
From the iconic Gulab Jamun and Rasgulla to the intricate Kaju Katli and the aromatic Peda, Indian delicious sweets are a testament to the country’s culinary heritage and its ability to blend flavors, techniques, and traditions into delightful confections.
Types of Indian Sweets
Certainly! There are numerous types of delicious Indian sweets, each with its own unique flavors, textures, and preparation methods.
Here are some popular types of Indian sweets:
- Gulab Jamun: Deep-fried milk-based dough balls soaked in sugar syrup, often flavored with cardamom or rose water.
- Jalebi: Deep-fried batter spirals soaked in saffron-infused sugar syrup, offering a sweet and tangy taste.
- Barfi: A fudge-like sweet made from condensed milk, sugar, and various flavorings such as nuts, saffron, and cardamom.
- Ladoo: Round sweets made from ingredients like chickpea flour, semolina, or various flours, often mixed with ghee, sugar, and nuts.
- Rasgulla: Soft cheese balls made from paneer (Indian cottage cheese) and soaked in sugar syrup, originating from Bengal.
- Halwa: A dense and rich sweet dish made from ingredients like semolina, carrots, lentils, or wheat, often garnished with nuts.
- Kaju Katli: A delicacy made from ground cashew nuts and sugar, often garnished with edible silver or gold foil.
- Peda: Soft, milk-based sweets flavored with cardamom, saffron, or other spices, typically garnished with nuts.
- Mysore Pak: A crumbly and rich sweet made from chickpea flour, ghee, and sugar, originating from the city of Mysore.
- Rasmalai: Soft cheese dumplings served in a creamy saffron-flavored milk, often garnished with pistachios.
- Sandesh: A Bengali sweet made from fresh paneer (cottage cheese), often flavored with cardamom, saffron, or fruits.
- Cham Cham: Oval-shaped sweets made from paneer, soaked in sugar syrup, and sometimes rolled in coconut flakes.
- Gajar Halwa: A dessert made from grated carrots cooked with milk, ghee, and sugar, often garnished with nuts.
- Malai Kulfi: A dense, frozen dessert similar to ice cream, made with condensed milk and flavored with cardamom, saffron, or nuts.
- Modak: A sweet dumpling often associated with the Ganesh Chaturthi festival, filled with coconut, jaggery, and nuts.
These are just a few examples of the many delightful Indian sweets that showcase the diverse flavors, ingredients, and culinary traditions of India.

Benefits of Indian Sweets
While Indian delicious sweets are known for their indulgent and delightful flavors, they also offer certain benefits, especially when consumed in moderation and as part of a balanced diet.
Here are some potential benefits of Indian sweets:
- Rich Source of Energy: Indian sweets are often made with ingredients like ghee, nuts, and sugars, which provide quick and sustained energy. This can be particularly beneficial during times when an energy boost is needed.
- Cultural and Social Significance: Sweets play an essential role in Indian culture, often being shared during celebrations, festivals, and social gatherings. They facilitate bonding, hospitality, and the expression of goodwill.
- Nutrient-Rich Ingredients: Many Indian sweets contain ingredients like milk, nuts, and spices that offer essential nutrients such as protein, calcium, vitamins, and healthy fats.
- Mood Enhancement: Sweets can trigger the release of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with mood regulation, leading to a temporary sense of pleasure and happiness.
- Increased Caloric Intake: For individuals who struggle with meeting their daily calorie intake, especially in a vegetarian or plant-based diet, Indian sweets can provide a concentrated source of calories.
- Traditional Medicine Benefits: Some Indian sweets contain ingredients like cardamom, saffron, and nuts, which are believed to have medicinal properties in traditional Ayurvedic and Unani medicine.
- Offering Essential Nutrients: Sweets made from milk products offer calcium, a vital nutrient for bone health, and proteins that contribute to overall growth and maintenance of the body.
- Shared Joy and Celebration: The act of sharing and enjoying Indian sweets can lead to positive social interactions, which can contribute to mental well-being.
- Moderation and Balance: Enjoying sweets in moderation allows individuals to satisfy their sweet cravings without drastically disrupting their overall dietary balance.
- Cultural Diversity: Indian sweets represent the diverse regional cuisines of India, showcasing different ingredients, cooking techniques, and cultural practices.
- Symbolism and Tradition: Sweets are often used as offerings in religious ceremonies and rituals, symbolizing devotion, blessings, and auspiciousness.
It’s important to note that the benefits of Indian sweets can be maximized when they are consumed as part of a well-rounded and balanced diet. Excessive consumption of sweets high in sugars and unhealthy fats can contribute to health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and dental problems. As with any food, portion control and moderation are key to enjoying the positive aspects of Indian sweets while maintaining overall health and well-being.
What sweets have the longest shelf life?
Sweets with lower moisture content, higher sugar concentration, and ingredients that are naturally preservative can typically have the longest shelf life.
Here are some examples of Indian sweets that tend to have a longer shelf life:
- Dry Fruit-Based Sweets: Sweets made primarily from dried fruits and nuts, such as various types of barfi (like kaju katli made from cashews) or chikki (brittle made from nuts and jaggery), have a longer shelf life due to their low moisture content.
- Besan Ladoo: Ladoos made from roasted chickpea flour (besan), ghee, sugar, and nuts tend to have a longer shelf life as they are relatively dry and have a balanced sugar content.
- Poha Chivda: A savory snack made from flattened rice (poha), nuts, spices, and dried fruits, poha chivda can stay fresh for quite some time due to its low moisture and high salt content.
- Sohan Halwa: This dense and rich halwa made from wheat flour, ghee, sugar, and nuts has a relatively longer shelf life because of its dense and dehydrated texture.
- Sukha Peda: These dry pedas, made with milk solids (khoya), sugar, and cardamom, have a longer shelf life compared to their moist counterparts.
- Besan Burfi: Burfi made from besan (chickpea flour), sugar, and ghee has a lower moisture content and can be stored for a relatively longer time.
- Nankhatai: These eggless shortbread cookies made from flour, ghee, sugar, and cardamom have a decent shelf life due to their lower moisture and fat content.
- Dry Coconut Barfi: Barfi made from desiccated coconut, sugar, and nuts can last longer due to the desiccated coconut’s low moisture content.
It’s important to remember that while these sweets tend to have longer shelf lives, the actual duration of preservation can vary depending on factors like the specific recipe, storage conditions, and the presence of any preservatives. Always store sweets in clean, airtight containers in a cool and dry place to maximize their shelf life. If you’re looking to store sweets for an extended period, consider using techniques like vacuum sealing or freezing to maintain their quality.

How do you preserve sweets for a long time?
Preserving Indian sweets for a longer shelf life involves using appropriate techniques to prevent spoilage and maintain their taste and texture over time.
Here are some methods to consider:
- Drying: Sweets that have lower moisture content can be preserved for longer periods. Sweets like dry fruit-based barfis or dry fruit chikkis fall into this category.
- Sugar Syrup: Some sweets like rasgulla or gulab jamun are preserved by keeping them soaked in sugar syrup. The high sugar concentration acts as a preservative.
- Vacuum Sealing: Vacuum-sealing can remove air from packaging, which helps in preventing the growth of microorganisms that cause spoilage. This method is often used for sweets with lower moisture content.
- Canning and Bottling: Some sweets, especially those made with fruits or jams, can be preserved in sterilized jars or cans. Sealing them while hot and creating a vacuum can prevent contamination.
- Refrigeration: Refrigeration can extend the shelf life of many sweets. However, it’s important to ensure proper packaging to prevent moisture absorption and flavor transfer.
- Freezing: Freezing is a very effective way to preserve sweets for extended periods. Sweets like kaju katli, barfi, or certain types of halwa can be frozen. Wrap them tightly in plastic wrap or aluminum foil, place in a freezer-safe container, and label with a date.
- Dehydration: Dehydrated sweets like sukha peda or dried fruit-based sweets can be stored in airtight containers in a cool, dry place.
- Air-Tight Containers: Using airtight containers is essential to prevent moisture and air from entering, which can lead to spoilage. This method is particularly useful for dry sweets like ladoos.
- Desiccants: Placing moisture-absorbing packets or desiccants inside the storage container can help maintain the texture and prevent moisture-related issues.
- Wrapping: Wrap individual sweets in wax paper or parchment paper and store them in layers inside an airtight container to prevent sticking and maintain freshness.
- Use of Preservatives: In some cases, small amounts of food-safe preservatives can be added to extend the shelf life of sweets. However, this should be done carefully and within recommended limits.
It’s important to note that the longevity of preserved sweets can vary based on factors like ingredients used, moisture content, and storage conditions. Always refer to specific recipes or local culinary traditions for guidance on the best preservation methods for the particular type of sweet you want to store.
Junk Food Impacts Advantages Effects & More
World’s most Nutritious and Healthy foods
If you don’t like this article/post please share your feedback.