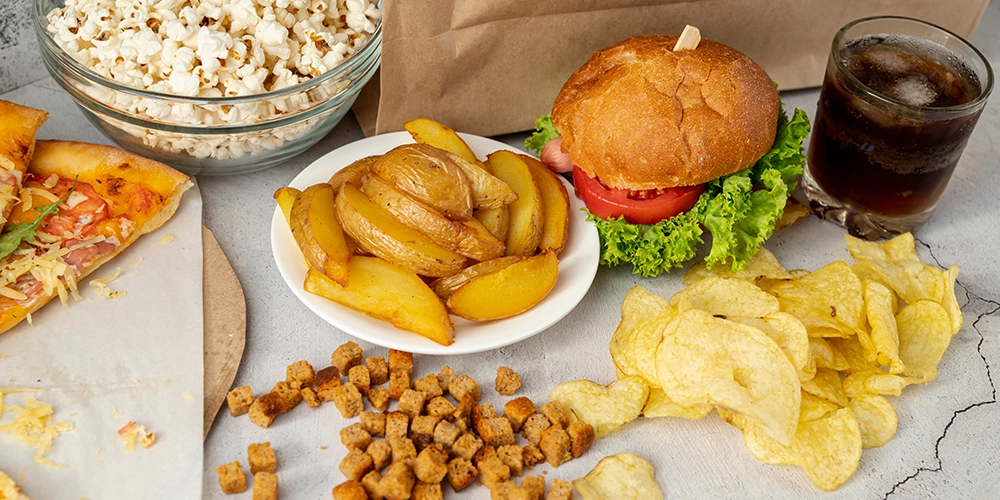
Fat foods: or “fat-rich foods” refer to foods that are high in dietary fat content. Dietary fat is one of the three macronutrients essential for human nutrition, alongside carbohydrates and protein. Fat is a concentrated source of energy, and it plays several important roles in the body.
Types of Fat Foods
Dietary fats can be categorized into different types based on their chemical structure.
Here are the primary types of dietary fats:
- Saturated Fats: These fats are typically solid at room temperature and are often found in animal products, such as red meat, poultry, and full-fat dairy products. They are also present in some tropical oils like coconut oil and palm oil. Consuming too much saturated fat may raise LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels in the blood, increasing the risk of heart disease.
- Trans Fats: Trans fats are artificially created fats through a process called hydrogenation, which makes liquid oils more solid. Trans fats are commonly found in some processed and packaged foods, like fried foods, baked goods (cakes, cookies, pastries), and some margarine products. Trans fats are known to raise LDL cholesterol and should be limited in the diet as they are associated with an increased risk of heart disease.
- Monounsaturated Fats: These fats are considered heart-healthy and are found in foods like olive oil, avocados, nuts (e.g., almonds, peanuts), and seeds (e.g., sunflower seeds). Monounsaturated fats can help lower LDL cholesterol levels when consumed in place of saturated and trans fats.
- Polyunsaturated Fats: These fats include omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which are essential for the body and must be obtained from the diet. Sources of polyunsaturated fats include fatty fish (e.g., salmon, mackerel), flaxseeds, walnuts, and some vegetable oils (e.g., soybean oil, corn oil). Omega-3 fatty acids, in particular, have been associated with various health benefits, including heart health and reducing inflammation.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids are a specific type of polyunsaturated fat known for their health benefits. They are found in fatty fish (e.g., salmon, sardines), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. Omega-3s are linked to improved heart health and may have anti-inflammatory properties.
It’s important to note that while dietary fat is an essential part of a balanced diet, it should be consumed in moderation, and the focus should be on choosing healthier fats like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats while limiting saturated and trans fats. The overall quality of your diet and the balance of nutrients are crucial for maintaining good health.
Benefits of Fat Foods
Consuming healthy fats as part of a balanced diet offers several benefits to your overall health and well-being.
Here are some of the benefits of including healthy fats in your diet:
- Energy Source: Fats are a concentrated source of energy, providing more calories per gram than carbohydrates or protein. They serve as a long-lasting and sustainable source of energy, helping to maintain energy levels throughout the day.
- Nutrient Absorption: Certain vitamins and phytonutrients are fat-soluble, meaning they require dietary fat for absorption. Healthy fats facilitate the absorption of vitamins A, D, E, and K, as well as various antioxidants and phytonutrients from fruits and vegetables.
- Heart Health: Unsaturated fats, particularly monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, have been associated with improved heart health. They can help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, reduce inflammation, and lower the risk of heart disease.
- Brain Function: Omega-3 fatty acids, a type of polyunsaturated fat, are essential for brain health and function. They may support cognitive function, memory, and mood stability. Fatty fish like salmon and walnuts are good sources of omega-3s.
- Cell Structure: Fats are a fundamental component of cell membranes and play a crucial role in maintaining cell structure and function. They contribute to cell integrity and help regulate cell signaling.
- Healthy Skin and Hair: Healthy fats help maintain the integrity of the skin barrier, keeping it moisturized and preventing dryness. Omega-3 fatty acids, in particular, can benefit skin health and may help reduce inflammation associated with skin conditions.
- Satiety and Appetite Control: Including healthy fats in your meals can contribute to a feeling of fullness and satiety, reducing the likelihood of overeating and snacking between meals.
- Balanced Hormones: Dietary fats are essential for the production of hormones, including sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone). A well-balanced intake of fats is necessary for hormonal balance.
- Weight Management: Contrary to the misconception that eating fat leads to weight gain, consuming moderate amounts of healthy fats can actually support weight management. Fats help you feel full and satisfied, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
- Joint Health: Omega-3 fatty acids may have anti-inflammatory properties that can benefit joint health. They may help reduce symptoms of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
It’s important to emphasize that while healthy fats offer numerous benefits, it’s equally important to moderate your fat intake and choose the right types of fats. Focus on incorporating sources of monounsaturated fats (e.g., olive oil, avocados) and polyunsaturated fats (e.g., fatty fish, nuts, seeds) into your diet while limiting saturated and trans fats, which are less healthy for your heart and overall health. Balance and variety in your diet are key to reaping the benefits of fats while maintaining a healthy lifestyle.

Why do we need fat foods?
We need fat-containing foods in our diet for several important reasons, as fats play various essential roles in
maintaining overall health and well-being:
- Energy Source: Dietary fats are a concentrated source of calories, providing more energy per gram (9 calories per gram) than carbohydrates and protein (4 calories per gram each). Fats serve as a valuable and long-lasting energy reserve that the body can draw upon when needed.
- Nutrient Absorption: Fat is necessary for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) and certain phytonutrients from fruits and vegetables. Without dietary fat, these nutrients may not be effectively absorbed by the body.
- Cell Structure: Fats are an integral part of cell membranes. They help maintain the integrity and fluidity of cell membranes, which is essential for proper cell function and communication.
- Hormone Production: Fats are essential for the synthesis of various hormones, including sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone) and regulatory hormones. Hormones play a critical role in processes like growth, reproduction, and metabolism.
- Insulation and Protection: Fat serves as an insulating layer under the skin, helping to regulate body temperature. It also cushions and protects vital organs, such as the heart and kidneys.
- Brain Function: The brain contains a significant amount of fat, and fats, particularly omega-3 fatty acids, are essential for optimal brain development and function. Omega-3s have been associated with improved cognitive function, memory, and mood stability.
- Satiety and Appetite Control: Consuming foods that contain healthy fats can contribute to a feeling of fullness and satisfaction after meals, which can help control appetite and reduce the likelihood of overeating.
- Skin and Hair Health: Healthy fats help maintain the integrity of the skin barrier, preventing dryness and promoting skin and hair health. They may also have anti-inflammatory effects that benefit the skin.
- Heart Health: While certain types of fats, like saturated and trans fats, can be harmful to heart health when consumed in excess, healthy fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, can have a positive impact. They can help lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart disease.
It’s important to emphasize that not all fats are created equal. While we need fats in our diet, it’s crucial to focus on consuming healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish, while limiting the intake of saturated and trans fats, which can be detrimental to health when consumed in excess. Achieving a balanced intake of fats, along with other essential nutrients, is key to maintaining overall health and well-being.
What happens when we eat fat food ?
When you eat foods that are high in fat, several physiological processes occur in your body to digest and metabolize the fat. The effects of consuming fat-rich foods can vary depending on the type of fat (healthy or unhealthy), the amount consumed, and your individual metabolism.
Here’s what generally happens when you eat foods rich in dietary fat:
- Digestion and Absorption: Dietary fat is initially broken down in the stomach and then emulsified in the small intestine with the help of bile produced by the liver. This process allows fat to mix with water and be broken into smaller particles. Pancreatic enzymes further break down these particles into fatty acids and glycerol, which can be absorbed into the bloodstream.
- Energy Production: The fatty acids and glycerol released from digested fats are transported via the bloodstream to cells throughout your body. There, they can be used for energy production. Fat is a dense source of calories and provides a long-lasting source of energy when needed.
- Nutrient Absorption: Fat aids in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K) and certain phytonutrients. These nutrients are better absorbed when consumed with some dietary fat.
- Hormone Regulation: Fats play a role in the production of hormones. They are essential for the synthesis of hormones such as sex hormones (estrogen and testosterone) and other regulatory molecules.
- Satiety and Appetite Control: Consuming foods with a reasonable amount of healthy fats can help you feel full and satisfied after a meal. This can contribute to better appetite control and potentially reduce overeating.
- Cholesterol Levels: The type of fat you consume can impact your cholesterol levels. Saturated and trans fats, when consumed in excess, can raise LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart disease. On the other hand, monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats can have a more positive effect on cholesterol levels when consumed in moderation.
- Weight Management: While fats are calorie-dense, including moderate amounts of healthy fats in your diet can actually support weight management by providing satiety and reducing the likelihood of snacking on less healthy options.
- Long-Term Health: A diet high in unhealthy fats, such as saturated and trans fats, can increase the risk of various health problems, including heart disease, obesity, and type 2 diabetes. Conversely, a diet rich in healthy fats, like monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, can have positive long-term health effects, including improved heart health and reduced inflammation.
It’s important to note that the effects of consuming fat-rich foods can vary from person to person based on factors like genetics, overall diet, and lifestyle. For optimal health, it’s recommended to focus on consuming healthy fats in moderation, while limiting saturated and trans fats to reduce the risk of chronic diseases. Balancing your fat intake with a variety of other nutrients is key to maintaining a well-rounded and nutritious diet.
Junk Food Impacts Advantages Effects & More
World’s most Nutritious and Healthy foods
If you don’t like this article/post please share your feedback.