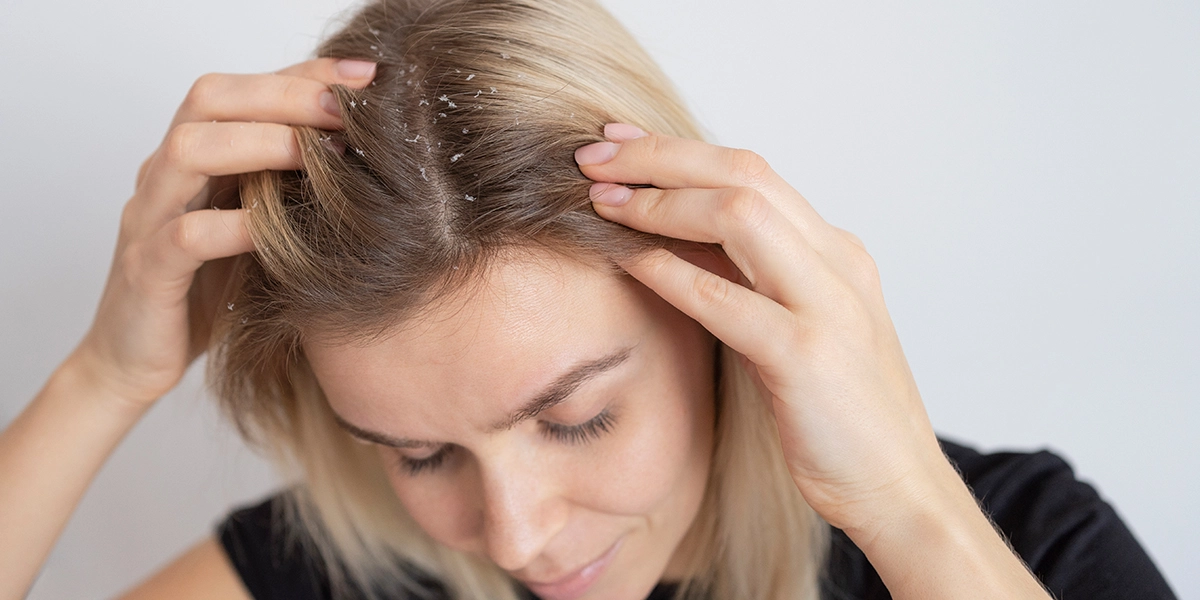
Dandruff: is a common skin condition that affects the scalp, causing the skin to become dry, flaky, and itchy. It is characterized by the shedding of dead skin cells from the scalp, which can lead to the visible presence of white or yellowish flakes in the hair and on clothing.
Types of Dandruff
Dandruff is generally classified based on its underlying causes and characteristics.
Here are some common types of dandruff:
- Dry Scalp Dandruff: This type of dandruff is often caused by dry skin on the scalp. It results in small, white flakes that are generally not oily. Dry scalp dandruff can be exacerbated by factors such as cold weather, low humidity, and excessive shampooing.
- Oily Scalp Dandruff: Also known as seborrheic dermatitis, this type of dandruff is associated with an overproduction of sebum (skin oil) on the scalp. It leads to larger, yellowish, or greasy flakes that can stick to the scalp and hair. Oily scalp dandruff is often accompanied by redness and itching.
- Fungal Dandruff: Fungal dandruff is caused by an overgrowth of a naturally occurring yeast called Malassezia. This yeast feeds on the sebum produced by the scalp and can lead to irritation, inflammation, and flaking. Fungal dandruff is usually accompanied by itching and can contribute to conditions like seborrheic dermatitis.
- Psoriasis-Related Dandruff: Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin condition that can affect the scalp, leading to the development of thick, silvery scales and dry, flaky patches. Psoriasis-related dandruff can be more persistent and may require specialized treatment.
- Contact Dermatitis-Related Dandruff: Certain hair care products, such as shampoos, conditioners, or hair dyes, can cause an allergic reaction or irritate the scalp, leading to dandruff-like symptoms. This is known as contact dermatitis.
- Medical Conditions-Associated Dandruff: Underlying medical conditions like eczema or other inflammatory skin conditions can cause dandruff-like symptoms on the scalp.
It’s important to note that the distinction between these types of dandruff is not always clear-cut, as some individuals may experience a combination of factors contributing to their dandruff. If you’re unsure about the specific type of dandruff you have or if your symptoms are severe, it’s recommended to consult a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of Dandruff
Dandruff is characterized by a range of symptoms that primarily affect the scalp.
Common symptoms of dandruff include:
- Flaking: The most noticeable symptom of dandruff is the shedding of white or yellowish flakes of dead skin from the scalp. These flakes may be small and fine or larger and more noticeable, depending on the severity of the condition.
- Itching: Dandruff often causes itching and discomfort on the scalp. The itching can range from mild to intense and can lead to scratching, which may further irritate the scalp.
- Dryness: The affected scalp may appear dry and feel tight. This dryness can contribute to the flaking and itching associated with dandruff.
- Redness: In some cases, dandruff can cause the scalp to become red and inflamed. This is particularly common in conditions like seborrheic dermatitis.
- Oily Scalp: While dandruff is often associated with dryness, it can also be accompanied by excessive oiliness on the scalp. This is especially true in cases of seborrheic dermatitis, where the scalp produces an excess of sebum.
- Scalp Sensitivity: People with dandruff may experience heightened sensitivity on the scalp, which can make it uncomfortable to touch or brush the hair.
- Hair Loss: In some cases, persistent dandruff and scratching of the scalp can lead to hair loss. This is more likely to occur if the dandruff is severe and untreated.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can vary in intensity from person to person and may also be influenced by the underlying cause of the dandruff. If you’re experiencing persistent or severe dandruff symptoms, it’s advisable to seek guidance from a dermatologist or medical professional who can provide an accurate diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Causes of Dandruff
Dandruff can have several underlying causes, and it is often the result of a combination of factors.
Some of the main causes of dandruff include:
- Malassezia Yeast: Malassezia is a type of yeast that naturally resides on the scalp. An overgrowth of this yeast can lead to dandruff. Malassezia feeds on the oils produced by the hair follicles, and its byproducts can cause irritation and flaking of the scalp.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: This is a common skin condition that can affect areas with a high concentration of oil glands, such as the scalp, face, and upper chest. It is characterized by redness, itching, and flaking. Seborrheic dermatitis is believed to be related to the immune system’s response to Malassezia yeast.
- Dry Skin: Dry skin on the scalp can lead to flaking and dandruff. Cold weather, low humidity, and frequent shampooing can contribute to dry skin.
- Sensitivity to Hair Products: Certain hair care products, particularly those containing harsh chemicals or fragrances, can irritate the scalp and lead to dandruff-like symptoms.
- Not Shampooing Enough: Infrequent shampooing or inadequate scalp hygiene can cause a buildup of oils, dead skin cells, and dirt on the scalp, leading to dandruff.
- Medical Conditions: Conditions like psoriasis, eczema, and other inflammatory skin disorders can affect the scalp and lead to dandruff-like symptoms.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, or certain medical conditions, can influence the production of skin oils and contribute to dandruff.
- Stress: Stress can have various effects on the body, including on the skin. It may exacerbate existing skin conditions or contribute to dandruff.
- Diet and Nutrition: Poor diet and lack of essential nutrients can affect the health of the skin, including the scalp. While diet is not a direct cause of dandruff, it can influence overall skin health.
- Genetics: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to developing dandruff or certain skin conditions that contribute to it.
It’s important to note that the exact cause of dandruff can vary from person to person, and individuals may experience a combination of these factors. If you’re experiencing persistent or severe dandruff, consulting a dermatologist can help identify the underlying cause and guide you toward effective treatment options.
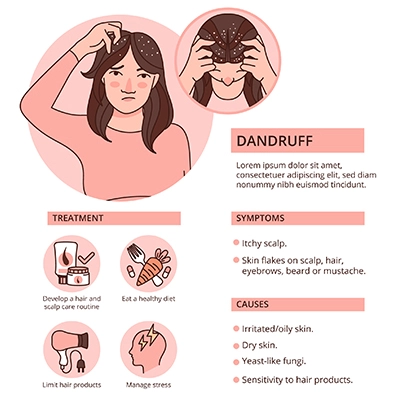
Prevention of Dandruff
While dandruff can be a common and persistent issue for some individuals, there are several steps you can take to help prevent or minimize its occurrence.
Here are some tips for preventing dandruff:
- Maintain Good Scalp Hygiene: Regularly wash your hair and scalp with a mild shampoo to remove excess oils, dead skin cells, and dirt. However, avoid over-washing, as this can lead to dryness and potentially worsen dandruff.
- Use the Right Shampoo: Choose a shampoo specifically formulated to address dandruff. Look for active ingredients such as zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, ketoconazole, or salicylic acid. These ingredients can help control the yeast that contributes to dandruff and reduce flaking.
- Massage Your Scalp: Gently massage your scalp while shampooing to help improve blood circulation and remove dead skin cells. Avoid scratching vigorously, as this can irritate the scalp.
- Manage Stress: Stress can exacerbate various skin conditions, including dandruff. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, exercise, or hobbies you enjoy.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids can contribute to healthy skin. Incorporate foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fish into your diet.
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water to keep your skin hydrated, including your scalp.
- Avoid Harsh Hair Products: Some hair care products, particularly those containing strong chemicals or fragrances, can irritate the scalp. Opt for gentle, hypoallergenic products.
- Protect from Harsh Weather: Cold, dry weather can contribute to dry scalp. Wear a hat or protect your head from extreme weather conditions.
- Limit Heat Styling: Excessive use of hairdryers, straighteners, and other heat styling tools can contribute to scalp dryness. Use these tools on a lower setting and avoid direct heat on the scalp.
- Get Regular Sunlight: Sunlight can help regulate the growth of Malassezia yeast. However, be sure to protect your skin from excessive sun exposure.
- Consult a Dermatologist: If your dandruff is persistent, severe, or not responding to over-the-counter treatments, consult a dermatologist. They can provide personalized advice and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Remember that individual factors and genetics can play a role in dandruff development. If you’re unsure about the best approach to prevent or manage your dandruff, seeking professional guidance is always a good idea.
What is The Main Cause of Hair Dandruff ?
The main cause of dandruff is believed to be an overgrowth of a yeast called Malassezia on the scalp. Malassezia is a normal part of the skin’s microbiome, but when it proliferates excessively, it can lead to skin irritation and inflammation, resulting in dandruff. The exact mechanisms by which Malassezia contributes to dandruff are not fully understood,
but researchers have identified several factors that play a role:
- Sebum Breakdown: Malassezia yeast thrives on the oils (sebum) produced by the hair follicles. As it breaks down these oils, it produces byproducts that can irritate the scalp and trigger an immune response, leading to flaking and itching.
- Inflammatory Response: The presence of Malassezia and its byproducts can stimulate the immune system, causing inflammation in the scalp. This inflammation contributes to the redness, itching, and flaking characteristic of dandruff.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to developing dandruff. If you have a family history of dandruff, you may be more likely to experience it yourself.
- Skin Barrier Dysfunction: In individuals with dandruff, there may be a disruption in the skin’s barrier function, allowing Malassezia to penetrate more deeply into the skin and trigger an immune response.
It’s important to note that while Malassezia is a major contributor to dandruff, other factors such as dry skin, sensitivity to hair products, hormonal changes, stress, and underlying skin conditions like seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis can also play a role in dandruff development.
Effective management and prevention of dandruff often involve addressing the overgrowth of Malassezia and managing any underlying factors that contribute to its growth and the associated inflammation. Using appropriate anti-dandruff shampoos and maintaining good scalp hygiene are key strategies for controlling dandruff symptoms. If you’re experiencing persistent or severe dandruff, it’s advisable to consult a dermatologist for proper diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
How Can I Stop Dandruff Fast ?
While there’s no instant cure for dandruff, there are several steps you can take to help alleviate dandruff symptoms and reduce their visibility. Keep in mind that results may vary from person to person, and it may take some time to see noticeable improvement.
Here are some tips to help you address dandruff quickly:
- Use an Anti-Dandruff Shampoo: Choose an anti-dandruff shampoo that contains active ingredients such as zinc pyrithione, selenium sulfide, ketoconazole, or salicylic acid. These ingredients can help control the growth of Malassezia yeast and reduce flaking. Use the shampoo as directed on the label, typically a few times a week.
- Massage Scalp: While shampooing, gently massage your scalp with your fingertips to help loosen and remove dead skin cells and excess oil.
- Avoid Over-Shampooing: While it’s important to keep your scalp clean, over-shampooing can strip the scalp of its natural oils, leading to dryness and potentially worsening dandruff. Find a balance that works for your hair type and scalp condition.
- Use Warm Water: When washing your hair, use lukewarm water instead of hot water, as hot water can strip the scalp of moisture.
- Exfoliate: Periodically use a gentle exfoliating scalp scrub or brush to help remove dead skin cells and prevent their buildup.
- Moisturize: After shampooing, use a lightweight, oil-free conditioner to keep the hair and scalp moisturized without adding excess oil.
- Avoid Harsh Hair Products: Steer clear of hair care products that contain harsh chemicals or fragrances that can irritate the scalp.
- Healthy Diet: Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and omega-3 fatty acids, as nutrition can play a role in overall skin health.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-reduction techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, as stress can exacerbate dandruff.
- Consult a Dermatologist: If your dandruff is severe, persistent, or not responding to over-the-counter treatments, consider seeking professional advice from a dermatologist. They can recommend prescription-strength shampoos or other treatments to help manage your dandruff.
It’s important to be patient and consistent in your approach to managing dandruff. It may take a few weeks to see significant improvement, so give your chosen treatment regimen some time to work. If you experience any unusual or severe symptoms, or if your dandruff persists despite your efforts, consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
Dark Circles Under Eyes: Symptoms, Remedies & Prevention
Heart Attack: Types, Symptoms & Prevention
Eye Infections: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment
Vertigo: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Preventive
Hair Loss, Types, Symptoms, Prevention & Treatments
Knee Pain, Symptoms, Types & Self Management
Headaches: Details, Types, Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Obesity: Definition, Types, Prevention & Treatment
Read this Article Also:- Incredible Hair Masks For Dandruff That Actually Work
If you don’t like this article/post please share your feedback.